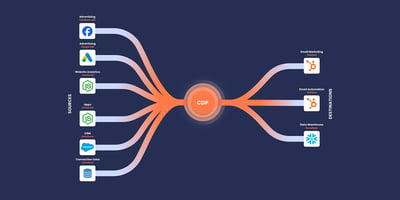
Can there be a single source of truth for customer data? Is it even conceivable? Customer data platforms (CDPs) certainly promise this, and I believe it is possible. Indeed, the technology exists, and it has become competent and affordable for businesses managing large datasets.
Introduction
I'm the CEO of MO Agency. We use a customer data platform called Segment at MO, but there are some other excellent CDPs available. To write this blog, I broadened my horizons by reading extensively about how Salesforce and Oracle describe and comprehend customer data platforms.
As a result, I've included summaries of their observations throughout. I hope this makes my blog more useful and does not promote my preferred CDP, Segment, but rather the concept of a CDP for improved customer engagement.
Understanding Customer Data Platforms
What is a CDP?
A customer data platform (CDP) is a specialised software system designed to centralise and unify customer data from a multitude of sources. This unification provides businesses with a comprehensive, singular view of each customer, enabling them to deliver more personalised experiences and targeted marketing campaigns. A CDP provides a source of truth for your customer data.
From Segment's perspective, a CDP consolidates data from various tools, such as social media platforms, company websites, email interactions, data warehouses, and more, to form a centralised customer database. This database encompasses all touchpoints and interactions a customer has with a product or service, allowing for more tailored marketing strategies and customer engagements.
Oracle further elaborates on the capabilities of a CDP by highlighting its ability to collect and unify first-party customer data. This includes a wide range of data types, from behavioural actions taken on websites and apps to transactional data like purchases and returns.
Lastly, Salesforce describes the CDP as a technology that not only aggregates customer data but also includes resources for multichannel campaigns and real-time customer interactions. The emphasis here is on the real-time aspect, ensuring businesses can engage with their customers promptly and relevantly.
Importantly, most of the data in CDPs is first-party data, which a company collects for marketing purposes. Third-party data, on the other hand, is bought or given between companies.
To make first-party data usable, CDPs integrate owned customer data by merging data points from many databases.

Summary
- Unified Customer Profile: CDPs create a comprehensive profile by combining data from various sources, ensuring a holistic view of each customer.
- Real-time Engagement: Modern CDPs, especially as described by Salesforce, focus on real-time data management, ensuring current and accurate customer information.
- Personalisation: With the unified data, CDPs enable businesses to offer hyper-personalised experiences across various touchpoints.
- First-Party Data: Data management, smart consumer analytics, and enhanced data protection and privacy are all advantages of CDPs.
In essence, a CDP serves as the backbone for customer data management, ensuring that businesses have a unified, coherent, and up-to-date understanding of their customers, which in turn facilitates better decision-making, targeted marketing, and enhanced customer experiences.
Important Definition:
What's the difference between a CDP and a CRM?
CDPs are an evolution of CRM systems, catering to the real-time, highly personalised needs of today's digital-first teams. In contrast, CRMs are a repository of known customer data and can be very siloed among departments, e.g., sales.
A CDP is not a replacement for a CRM.
A good CDP breaks down silos by connecting multiple data sources to build a real-time and holistic picture of your customer. Ideally, your CRM becomes an additional data source for your CDP.
This complete picture enables marketing teams to meet customers right where they are and with highly tailored messaging.
What are the benefits of a CDP?
A customer data platform offers many advantages to businesses, primarily centred around enhanced data management and improved customer engagement.
One of the main advantages, as highlighted by Segment, is CDPs' capacity to manage customer data in a systematic way. Businesses can gain insightful customer analytics by combining data from various touchpoints. This centralised method helps to improve data privacy and protection while also guaranteeing data accuracy.
Oracle emphasises the role of CDPs in delivering personalised services. By centralising and streamlining customer data, businesses can ensure they are compliant with data policies and regulatory standards and positioned to offer tailored experiences to their customers.
A CDP’s ability to continuously ingest new data means that businesses have an evolving history of customer interactions at their fingertips. This, in turn, empowers marketers to target the right customers with the right strategies, ensuring more efficient and effective marketing campaigns.
According to Salesforce, CDPs offer advantages that go beyond data management. They allow businesses to understand how specific consumers interact with different brands, products, and services, creating more opportunities for personalisation and cross-selling. Additionally, CDPs offer intuitive controls that make it simple for businesses to analyse customer data, create segments, and pinpoint key audiences.
Summary
To sum up the benefits:
- Organised Data Management: centralised storage and management of customer data, ensuring accuracy and protection.
- Enhanced Personalisation: Ability to offer tailored experiences based on comprehensive customer profiles
- Efficient Marketing: Streamlined campaigns target the right audience, leading to better returns on marketing investments.
- Insightful Analytics: A comprehensive view of customer journeys enables businesses to make data-driven decisions.
In summary, a CDP is an essential tool for companies looking to improve their customer engagement strategies. By providing a unified view of customers, ensuring data accuracy, and facilitating personalised interactions, CDPs position businesses to achieve their marketing goals and deliver exceptional customer experiences.
How do CDPs help solve fragmented customer experiences?
Customers now interact with businesses through a variety of channels, including social media, websites, emails, in-person interactions, and more. Data from each interaction is often stored in different systems, which often leads to fragmented and disjointed customer experiences.
Additionally, customers expect that you update their data and preferences as and when they make them known to you, regardless of the channel, in real-time. Whether they tell a customer service representative, visit a social media page, or send an email to change their email address or relationship status, they expect your subsequent communication to reflect that change in real-time.
The segment highlights that CDPs play a crucial role in consolidating this data from various tools and forming a centralised customer database. This unified database encompasses all touchpoints and interactions a customer has with a product or service, allowing businesses to have a holistic view of their customers.
Oracle expands on this further by highlighting the CDP's capacity to collect and harmonise first-party customer data from various sources. This covers a wide range of data types, including transactional information like purchases and returns, as well as browsing patterns on websites and mobile apps.
By connecting all the tools marketers use, CDPs act as a single source of truth for customer data. This ensures businesses can enforce and abide by data policies and regulatory standards while providing a comprehensive view of each customer.
The below diagram shows how data flows seamlessly and in real time from a company website, app, and CRM system to trigger relevant email automation. E.g. A confirmation that marriage status has been updated

The diagram below shows how the process works without a CDP. In this example, three people who each manage the data for the company website, app, and CRM need to export data and share it with another person (the fourth person!) who will upload it into the marketing system, HubSpot.
Then we have another problem. If that process happens monthly, there can be a 0-31 day delay or window for incorrect data to trigger an automated email.
This assumes all these very manual processes happen on time and without any errors. That's a large risk for customer satisfaction.

Salesforce describes the CDP as a technology that not only aggregates customer data but also includes resources for multichannel campaigns and real-time customer interactions. By acting as a central database for user-level data, CDPs connect databases that traditionally don't share data.
This makes sure that all departments within a company, including marketing, sales, and customer service, have access to the same comprehensive set of customer data.
Summary
- Unified Customer View: CDPs consolidate data from various sources, ensuring a holistic view of each customer and addressing the challenge of fragmented experiences.
- Real-time Data Management: Modern CDPs focus on real-time data management, ensuring that businesses can engage with their customers in a timely and relevant manner.
- Integration and Data Silos: CDPs act as a bridge, connecting databases that traditionally operate in isolation, ensuring seamless data sharing across platforms.
In essence, CDPs provide a solution to the challenge of fragmented customer experiences by centralising and unifying customer data. By offering a single, coherent, and up-to-date source of truth about customers, CDPs empower marketers to deliver consistent and personalised experiences across all touchpoints, ensuring enhanced customer engagement and satisfaction.
The Strategic Impact of CDPs on Marketing
Enhanced Customer Engagement with CDPs
With the advent of digital transformation, the marketing environment has changed, highlighting the need for companies to engage customers in a more personalised and coordinated way.
Understanding and accommodating unique customer needs and preferences is key to improving customer engagement. Segment emphasises the role CDPs play in making it easier to create a comprehensive customer view. A full understanding of their customers is given to marketers by CDPs, with them combining data from various touchpoints.
This unified perspective enables marketers to tailor their strategies, ensuring that communications are not only relevant but also consistent across various channels. Such personalised interactions foster deeper connections with customers, enhancing their overall experience with the brand.
Oracle and Salesforce both emphasise the strategic advantage of having a centralised system. In times of economic or industry challenges, having a unified view of customers can be a game-changer. It allows businesses to be agile, adapting their strategies based on real-time insights.
By breaking down internal siloes, CDPs ensure that all departments, from marketing to sales to customer service, are aligned in their approach. This streamlined communication strategy not only recession-proofs organisations but can also unlock new opportunities, positioning businesses to capitalise on emerging trends and customer behaviours.
Summary
Summarising the strategic impact on customer engagement:
- Personalised Interactions: With a comprehensive view of customers, marketers can tailor their strategies, ensuring relevance and consistency.
- Agility in Strategy: CDPs allow businesses to adapt quickly to changing economic landscapes, ensuring resilience and continued growth.
- Breaking Down Siloes: By centralising customer data, CDPs foster cross-departmental collaboration, ensuring a unified approach to customer engagement.
The strategic impact of centralising and integrating customer data is profound for marketers. It not only enhances customer engagement through personalised interactions but also positions businesses to navigate challenges and capitalise on opportunities.
Data Privacy: Addressing Data Challenges with a CDP
Navigating data privacy and compliance is a big concern for businesses, especially in an era where data privacy regulations are becoming increasingly stringent and the digital landscape is changing quickly.
One of the significant challenges that businesses face today is the phasing out of third-party cookies. This change disrupts traditional data collection methods, making it harder for businesses to track user behaviour and preferences.
With a CDP in place, businesses can still gain insights into customer behaviour and preferences without relying on third-party cookies, thanks to the centralisation of data from various first-party sources.
Beyond just first-party data, CDPs also assist in managing second-party and third-party data. This comprehensive approach to data management ensures that businesses can adapt to industry shifts. As the reliance on third-party data diminishes, businesses can leverage first-party and second-party data more effectively, ensuring that their marketing strategies remain relevant and effective.
Additionally, CDPs ensure businesses can adapt their data management practices to reflect industry shifts and remain compliant with evolving regulations by managing various data types.
Summary
To summarise how CDPs are shaping the future of data challenges posed by ever stricter Data Privacy regulations
- Navigating Third-party Cookie Loss: CDPs provide a solution to the challenges posed by phasing out third-party cookies, ensuring stable data collection methods.
- Managing Various Data Types: CDPs manage first-party, second-party, and third-party data, ensuring businesses adapt to industry shifts and changing regulations.
In summary, a CDP provides businesses with a powerful tool to help them navigate the difficulties presented by data privacy and compliance. CDPs ensure that organisations can continue to gain insights, drive marketing strategies, and ensure compliance with data privacy laws by centralising data, managing various data types, and providing stability in the face of industry shifts.
Data Privacy: Ensuring Compliance by using a CDP
For businesses today, navigating the complex landscape of data privacy and compliance is of utmost importance, particularly given the dynamic nature of privacy regulations around the world. In this situation, a customer data platform plays an essential and strategic role.
CDPs are designed to assist organisations in complying with current privacy regulations and preparing for future ones. This proactive approach is vital in a world where data privacy norms continuously evolve and non-compliance can lead to significant legal and reputational risks.
CDPs primarily focus on collecting first-party data, which is data that businesses collect directly from their customers. This includes data from website visits, app usage, email interactions, and purchases. With the decline of third-party cookies, first-party data has become even more valuable as it is consented to, accurate, and directly relevant to the business.
First-party data is generally considered more compliant as it's often obtained with clear consent from users. By focusing on first-party data and ensuring its proper management, CDPs provide businesses with a safeguard against potential breaches of data privacy norms.
Furthermore, the centralised nature of CDPs ensures that all customer data is stored, managed, and accessed from a singular platform. This centralisation simplifies the process of ensuring that data handling practices are in line with privacy regulations. It also makes it easier for businesses to implement changes in data management practices in response to new or updated regulations.
Summary
To summarise how CDPs are shaping the future of data privacy compliance:
- Proactive Compliance: CDPs assist businesses in adhering to current privacy regulations and preparing for upcoming ones, mitigating potential legal and reputational risks.
- First-party Data Focus: By emphasising the management of first-party data, CDPs ensure that businesses are better aligned with data privacy norms.
- Centralised Data Management: The unified nature of CDPs simplifies compliance efforts, ensuring consistent data handling practices across the organisation.
For businesses attempting to navigate the complexities of data privacy and compliance, a CDP serves as a fundamental tool. CDPs position businesses to ensure compliance, protecting them from potential risks and boosting customer trust by centralising data, emphasising first-party data management, and anticipating changing regulations.
The Wrap
In conclusion, the Customer Data Platform (CDP) stands as a transformative tool in the modern digital landscape. It promises a unified and singular source of truth for customer data, bridging the gaps between fragmented customer experiences and offering a comprehensive view of each customer's journey.
By centralising data from various touchpoints, CDPs not only enhance customer engagement through personalised interactions but also address the pressing challenges of data privacy and compliance.
As businesses grapple with the evolving digital ecosystem, the strategic importance of CDPs cannot be understated. They offer agility in strategy, ensure data accuracy, and foster a proactive approach to compliance, positioning businesses at the forefront of customer-centric innovation.
Whether it's Segment, Oracle, Salesforce, or another CDP entirely, the core essence of a CDP remains consistent: to provide businesses with a holistic understanding of their customers, facilitating improved decision-making, targeted marketing, and exceptional customer experiences.